pISSN : 3058-423X eISSN: 3058-4302
Open Access, Peer-reviewed

pISSN : 3058-423X eISSN: 3058-4302
Open Access, Peer-reviewed
Min Woo Park,Jun Suk Hong,Moo Kyu Suh,Gyoung Yim Ha
10.17966/JMI.2018.23.1.30 Epub 2018 April 01
Abstract
Keywords
Morphology Trichophyton mentagrophytes
Trichophyton (T.) mentagrophytes species are common causative pathogens for human and animal dermatophytoses with variable morphology, ecologic and genetic backgrounds[1],[2]. T. mentagrophytes causes tinea pedis, tinea unguium, and highly contagious tinea corporis and tinea capitis in human and tinea barbae is the classic form that presents mild to severe pustular folliculitis[3]. Anthoropophilic strains of T. mentgrophytes are T. mentagrophytes var. interdigitale, T. mentagrophytes var. nodulare, T. mentagrophytes var. goetzii, and zoophilic strains of T. mentagrophytes are T. mentagrophytes var. mentagrophytes, T. mentagrophytes var. granulosum (rodents), T. mentagrophytes var. erinacei (hedgehog), T. mentagrophytes var. quinckeanum (mice and camels)[2].
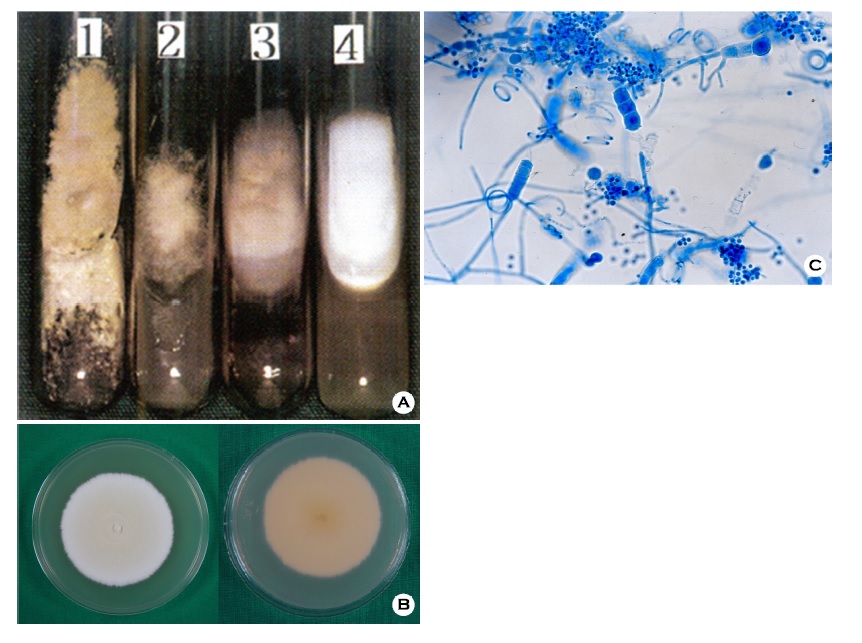
The colonies of T. mentagrophytes are variable, and divided into four subtypes; granular type, powdery type, persicolor type, downy type (Figure 1A). Anthropophilic isolates having a downy, powdery or fluffy texture, while zoophilic isolated was more granular in morphology (Figure 1B). The reverse side of colony shows various color from yellow to reddish brown (Figure 1B). Microscopic morphology of T. mentagrophytes shows microconidia are spherical to pyriform and macroconidia show cigar to club shaped (Figure 1C). Macroconidia have a smooth wall and between 3 to 8 septated cells and spiral or coiled hyphae may be presents[1]. Macroscopic morphology and microscopic examination may help identification of species, although it can be distinguished more accurately by using molecular biological analysis[2],[3].
In relation to this article, I declare that there is no conflict of interest.
References
1. De Hong GS, Guarro J, Gene J, Figueras MJ. Atlas of clinical fungi. 2nd ed. Virgili, Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures, 2000:965-970
Crossref
Google Scholar
2. Kim JA, Takahashi Y, Tanaka R, Fukushima K, Nishimura K, Miyaji M. Identification and subtyping of Trichophyton mentagrophytes by random amplified polymorphic DNA. Mycoses 2001;44:157-165
Crossref
Google Scholar
3. Symoens F, Jousson O, Planard C, Fratti M, Staib P, Mignon B, et al. Molecular analysis and mating behavior of the Trichophyton mentagrophytes species complex. Int J Med Microbiol 2011;301:260-266
Crossref
Google Scholar
Congratulatory MessageClick here!