pISSN : 3058-423X eISSN: 3058-4302
Open Access, Peer-reviewed

pISSN : 3058-423X eISSN: 3058-4302
Open Access, Peer-reviewed
Jisoo Kim,Taekwoon Kim,Jisung Kim,Joonsoo Park
10.17966/JMI.2023.28.1.19 Epub 2023 April 05
Abstract
Keywords
Fungal culture Plate medium Slant medium Trichophyton mentagrophytes
Trichophyton mentagrophytes is a zoophilic or anthro- pophilic dermatophyte, known as second most frequent causative agent of dermatophytosis after T. rubrum1,2. T. mentagrophytes are classified into granular type, powdery type, persicolor type, and downy type3.
Plate medium and slant medium employed in fungal culture have various advantages and disadvantages clinically. The plate medium is filled with agar and other substrates, and the shape, color, and morphology of the colony can be detected easily compared to the slant medium, making it more appro- priate for species identification. However, the drawback is a larger surface area than slant medium, so it is challenging to store for a long time due to faster evaporation, and a higher risk of contamination.
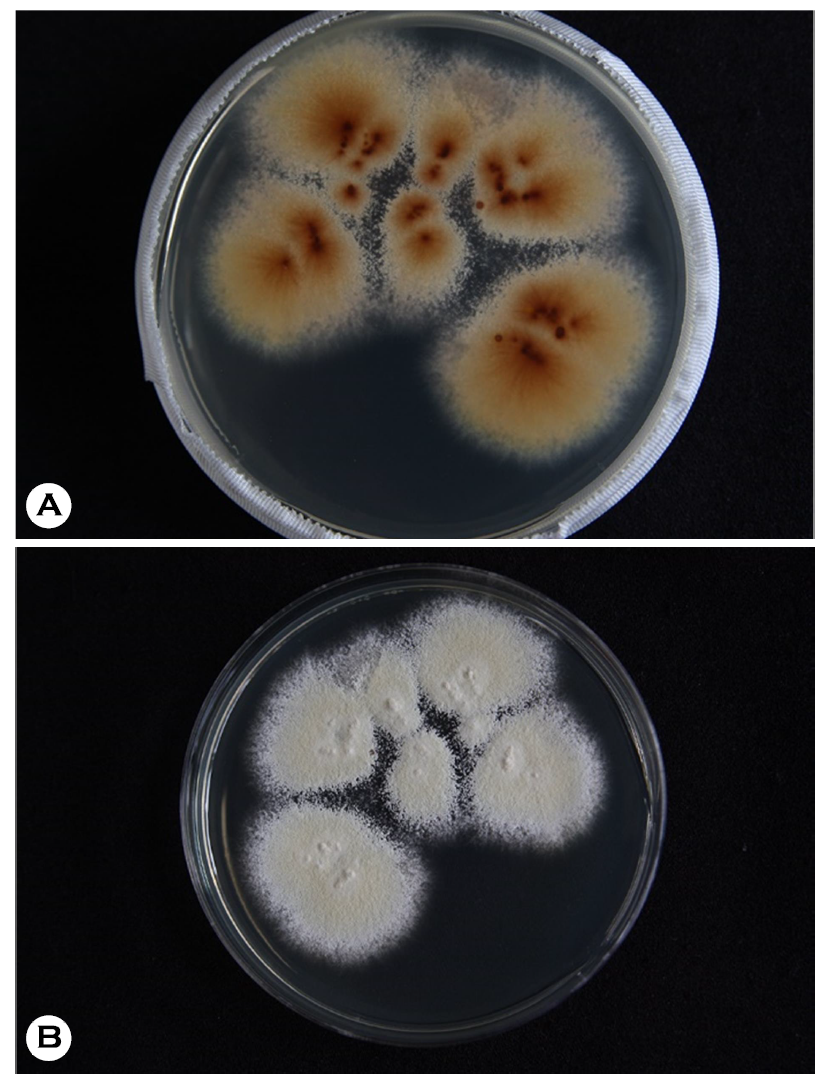
Fungal culture can be conducted in Sabouraud's dextrose agar, and yellowish-brown to reddish-brown reverse staining found on the plate medium is a characteristic finding of T. mentagrophytes (Fig. 1A). Furthermore, other plate medium results of T. mentagrophytes include: white to bright yellow or pink on the front (Fig. 1B) and red-brown to gray-yellow color on the reverse side. Periphery morphology is fine saw teeth shape.
Characteristic findings of T. mentagrophytes on plate medium are flat, white to cream, powdery to the granular colony on the frontal side, and reverse pigmentation which is yellow-brown to reddish-brown color on the reverse side. In particular, plate medium has more advantages for identifying T. mentagrophytes colony because the pattern on the back side cannot be found in slant medium. Therefore, plate media is better than slant medium when the clinician needs to identify and purify the colony.
References
1. Han JH, Lee JH, Lee JY, Park YM. Disseminated tinea corporis by Trichophyton mentagrophytes. Korean J Med Mycol 2015;20:102-108
Google Scholar
2. Kim JA, Takahashi Y, Tanaka R, Fukushima K, Nishimura K, Miyaji M. Identification and subtyping of Trichophyton mentagrophytes by random amplified polymorphic DNA. Mycoses 2001;44:157-165
Google Scholar
3. Kim WJ, Kim JG, Choi JH, Shin DH, Choi JS, Kim KH, et al. Classification and Typing of Trichophyton mentagrophytes Isolated from a Korean population. Korean J Med Mycol 2017;22:1-14
Google Scholar
Congratulatory MessageClick here!